

| Intersoft.Client.UI.ScheduleView Namespace > UXScheduleView Class : CanUserEditItems Property |
<CategoryAttribute("Common Properties")> Public Property CanUserEditItems As Boolean
Dim instance As UXScheduleView Dim value As Boolean instance.CanUserEditItems = value value = instance.CanUserEditItems
[CategoryAttribute("Common Properties")] public bool CanUserEditItems {get; set;}
[CategoryAttribute("Common Properties")] public: property bool CanUserEditItems { bool get(); void set ( bool value); }
Data editing in UXScheduleView involves three fundamental processes, Create, Update and Delete (CUD). You can enable each editing feature by setting the property CanUserAddItems, CanUserDeleteItems, CanUserEditItems, CanUserMoveItems, CanUserResizeItems.
| Enable Editing |
Copy Code
|
|---|---|
<Intersoft:UXScheduleView DisplayDate="1/2/2012" EventsSource="{Binding Events}" CategoriesSource="{Binding Categories}" ResourcesSource="{Binding Resources}" CanUserAddItems="True" CanUserDeleteItems="True" CanUserEditItems="True" CanUserMoveItems="True" CanUserResizeItems="True"> <Intersoft:UXScheduleDayView/> <Intersoft:UXScheduleWorkWeekView/> <Intersoft:UXScheduleWeekView IsActive="True"/> <Intersoft:UXScheduleMonthView/> </Intersoft:UXScheduleView> |
|
When the CanUserEditItems property is set to true, you can edit the event in UXScheduleView. To edit an event, first you need to select the event to edit, then you can choose one of the provided options to edit the event as follows.
 |
Editing a recurring pattern using the editing form will cause all the exception events to be deleted. |
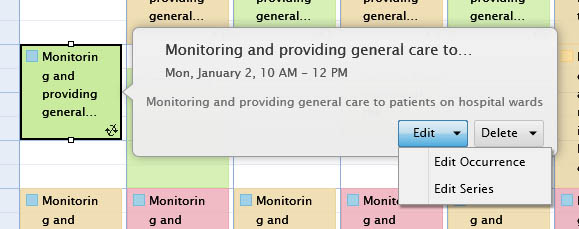

You can also use context menu to directly edit an existing event. In this case, the editing form will be shown instead of activating inline editing. 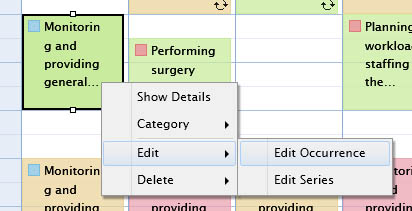
The context menu smartly adapts its commands depending on the type of selected event. The figure above illustrates the context menu when the selected event type is a recurring event.
Target Platforms: Windows 7, Windows Vista SP1 or later, Windows XP SP3, Windows Server 2008 (Server Core not supported), Windows Server 2008 R2 (Server Core supported with SP1 or later), Windows Server 2003 SP2