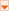
| Overload | Description |
|---|---|
| GetFormats() | Gets existing data formats available. |
| GetFormats(Boolean) | Gets existing data formats available. |
The following example code uses the GetFormats overload to get an array of strings denoting all data formats available in a data object.
| GetFormats |  Copy Code Copy Code |
|---|---|
string sourceData = "Some string data to store...";
byte[] unicodeText = Encoding.Unicode.GetBytes(sourceData);
byte[] utf8Text = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(sourceData);
string uniCodeFormat = "Unicode";
string utf8DataFormat = "UTF-8";
DragDropEventData dataObject = e.Data as DragDropEventData;
dataObject.SetData(sourceData);
dataObject.SetData(uniCodeFormat, unicodeText);
dataObject.SetData(utf8DataFormat, utf8Text);
// Get an array of strings, each string denoting a data format
// that is available in the data object. This overload of GetDataFormats
// returns all available data formats, native and auto-convertible.
string[] dataFormats = dataObject.GetFormats();
// Get the number of data formats present in the data object, including both
// auto-convertible and native data formats.
int numberOfDataFormats = dataFormats.Length;
// To enumerate the resulting array of data formats, and take some action when
// a particular data format is found, use a code structure similar to the following.
foreach (string dataFormat in dataFormats)
{
if (dataFormat == uniCodeFormat)
{
// Take some action if/when data in the Text data format is found.
break;
}
else if (dataFormat == utf8DataFormat)
{
// Take some action if/when data in the string data format is found.
break;
}
}
|
|
Because a single data object can contain an arbitrary number of data formats, data objects include facilities for retrieving a list of available data formats.
Target Platforms: Windows 98, Windows NT 4.0, Windows Millennium Edition, Windows 2000, Windows XP Home Edition, Windows XP Professional, Windows Server 2003 family, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 family